Osmium - 76Os: the essentials
- Name: osmium
- Symbol: Os
- Atomic number: 76
- Relative atomic mass (Ar): 190.23 (3) g [see note g]
- Standard state: solid at 298 K
- Appearance: bluish grey
- Classification: Metallic
- Group in periodic table: 8
- Group name: Precious metal or Platinum group metal
- Period in periodic table: 6
- Block in periodic table: d
- Shell structure: 2.8.18.32.14.2
- CAS Registry: 7440-04-2
Osmium atoms have 76 electrons and the shell structure is 2.8.18.32.14.2. The ground state electronic configuration of neutral osmium is [Xe].4f14.5d6.6s2 and the term symbol of osmium is 5D4.
Osmium: description
Ruthenium, rhodium, palladium, osmium, iridium, and platinum together make up a group of elements referred to as the platinum group metals (PGM).
Osmium metal is lustrous, bluish white, extremely hard, and brittle even at high temperatures. It has the highest melting point and lowest vapour pressure of the platinum group. The metal is very difficult to fabricate, but the powder can be sintered in a hydrogen atmosphere at a temperature of 2000°C. The solid metal is not affected by air at room temperature, but the powdered or spongy metal slowly gives off osmium tetroxide, which is a powerful oxidising agent and has a strong smell. The tetroxide is highly toxic, and boils at 130°C (760 mm). Concentrations in air as low as 10-7 g m-3 can cause lung congestion, skin damage, or eye damage.

This sample is from The Elements Collection, an attractive and safely packaged collection of the 92 naturally occurring elements that is available for sale.
Osmium: physical properties
Density of solid: 22610 kg m-3
Molar volume: 8.42 cm3
Thermal conductivity: 88 W m‑1 K‑1
Osmium: heat properties
Melting point: 3306 [3033 °C (5491 °F)] K
Boiling point: 5285 [5012 °C (9054 °F)] K
Enthalpy of fusion: 20.5 kJ mol-1
Osmium: atom sizes
Atomic radius (empirical): 130 pm
Molecular single bond covalent radius: 129 (coordination number 4) ppm
van der Waals radius: 241 ppm
Osmium: electronegativities
Pauling electronegativity: 2.2 (Pauling units)
Allred Rochow electronegativity: 1.52 (Pauling units)
Mulliken-Jaffe electronegativity: (no data)
Osmium: orbital properties
First ionisation energy: 814.17 kJ mol‑1
Second ionisation energy: 1640 kJ mol‑1
Third ionisation energy: 2410 kJ mol‑1
Osmium: abundances
Universe: 3 ppb by weight
Crustal rocks: 1.8 ppb by weight
Human: (no data) ppb by weight
Osmium: crystal structure

Osmium: biological data
Human abundance by weight: (no data) ppb by weight
Osmium has no biological role. Osmium oxide, OsO4, is highly toxic, and boils at 130°C (760 mm). Concentrations in air as low as 10-7 g m-3 can cause lung congestion, skin damage, and severe eye damage.
Osmium: uses
Osmium: reactions
Reactions of osmium as the element with air, water, halogens, acids, and bases where known.
Osmium: binary compounds
Binary compounds with halogens (known as halides), oxygen (known as oxides), hydrogen (known as hydrides), and other compounds of osmium where known.
Osmium: compound properties
Bond strengths; lattice energies of osmium halides, hydrides, oxides (where known); and reduction potentials where known.
Osmium: history
Osmium was discovered by Smithson Tennant in 1803 at England. Origin of name: from the Greek word "osme" meaning "smell".Osmium: isotopes
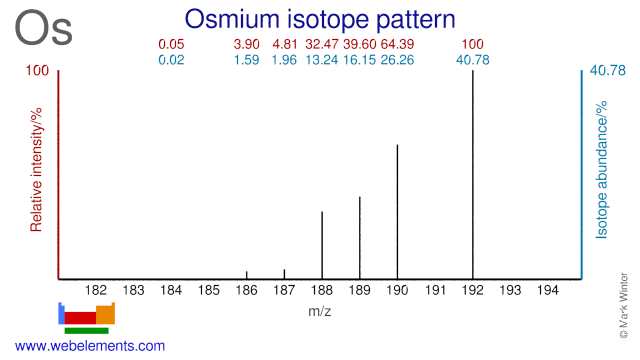
Osmium isotopes are used for the production of radioisotopes and in scientific experiments. Os-192 can be used for the production of the medical radioisotope Pt-195m. Os-184 is used for the production of the radioisotope Os-185. Os-191 can be used for the production of the radioisotopes Os-192. Os-190 has been used as a tracer to determine Os abundance in meteorites using isotope dilution ICP-MS. Finally, Os-189 has been used to experiment with nuclear excitation by electronic transition.
Osmium: isolation
Isolation: it would not normally be necessary to make a sample of osmium in the laboratory as the metal is available, at a price, commercially. The industrial extraction of osmium is complex as the metal occurs in ores mixed with other metals such as ruthenium, rhodium, palladium, silver, platinum, and gold. Sometimes extraction of the precious metals such as iridium, rhodium, platinum and palladium is the main focus of a partiular industrial operation while in other cases it is a byproduct. The extraction is complex because of the other metals present and only worthwhile since osmium is useful as a specialist metal and is the basis of some catalysts in industry.
Preliminary treatment of the ore or base metal byproduct is required to remove silver, gold, palladium, and platinum. The residue is melted with sodium bisulphate (NaHSO4) and the resulting mixture extracted with water to give a solution containing rhodium sulphate, Rh2(SO4)3. The insoluble residue contains the osmium. The residue is melted with Na2O2 and extracted into water to extract the ruthenium and osmium salts (including [RuO4]2- and [OsO4(OH)2]2-). The residue contains iridium oxide, IrO2. Reaction of the salt with chlorine gas gives the volatile oxides RuO4 and OsO4. The osmium oxide is dissolved by treatment with alcoholic sodium hydroxide to form Na2[OsO2(OH)4], and the osmium precipiated out as pure OsCl2O2(NH3)4 by treatment with NH4Cl. Evaporation to dryness and burning under hydrogen gas gives pure osmium.