Indium - 49In: the essentials
- Name: indium
- Symbol: In
- Atomic number: 49
- Relative atomic mass (Ar): 114.818 (1)
- Standard state: solid at 298 K
- Appearance: silvery lustrous grey
- Classification: Metallic
- Group in periodic table: 13
- Group name: (none)
- Period in periodic table: 5
- Block in periodic table: p
- Shell structure: 2.8.18.18.3
- CAS Registry: 7440-74-6
Indium atoms have 49 electrons and the shell structure is 2.8.18.18.3. The ground state electronic configuration of neutral indium is [Kr].4d10.5s2.5p1 and the term symbol of indium is 2P1/2.
Indium: description
Indium is a very soft, silvery-white metal with a brilliant lustre. The pure metal gives a high-pitched "scream" when bent. It wets glass, as does gallium. It is useful for making low-melting alloys. An alloy of 24% indium and 76% gallium is liquid at room temperature. Canada produces the majority of of the world's supply of indium.

Small and large samples of indium wire like this, as well as foil, and sheet, can be purchased from Advent Research Materials via their web catalogue.
Indium: physical properties
Density of solid: 7310 kg m-3
Molar volume: 15.76 cm3
Thermal conductivity: 82 W m‑1 K‑1
Indium: heat properties
Melting point: 429.75 [156.6 °C (313.88 °F)] K
Boiling point: 2345 [2072 °C (3762 °F)] K
Enthalpy of fusion: 20.5 kJ mol-1
Indium: atom sizes
Atomic radius (empirical): 155 pm
Molecular single bond covalent radius: 142 (coordination number 3) ppm
van der Waals radius: 243 ppm
Indium: electronegativities
Pauling electronegativity: 1.78 (Pauling units)
Allred Rochow electronegativity: 1.49 (Pauling units)
Mulliken-Jaffe electronegativity: 1.76 (sp2 orbital)
Indium: orbital properties
First ionisation energy: 558.30 kJ mol‑1
Second ionisation energy: 1820.72 kJ mol‑1
Third ionisation energy: 2705.85 kJ mol‑1
Indium: abundances
Universe: 0.3 ppb by weight
Crustal rocks: 160 ppb by weight
Human: (no data) ppb by weight
Indium: crystal structure
Indium: biological data
Human abundance by weight: (no data) ppb by weight
Indium has no biological role. In small doses it is said to stimulate the metabolism.
Indium: uses
Indium: reactions
Reactions of indium as the element with air, water, halogens, acids, and bases where known.
Indium: binary compounds
Binary compounds with halogens (known as halides), oxygen (known as oxides), hydrogen (known as hydrides), and other compounds of indium where known.
Indium: compound properties
Bond strengths; lattice energies of indium halides, hydrides, oxides (where known); and reduction potentials where known.
Indium: history
Indium was discovered by Ferdinand Reich, Hieronymus Theodor Richter in 1863 at Germany. Origin of name: named after the indigo line in its atomic spectrum.Indium: isotopes
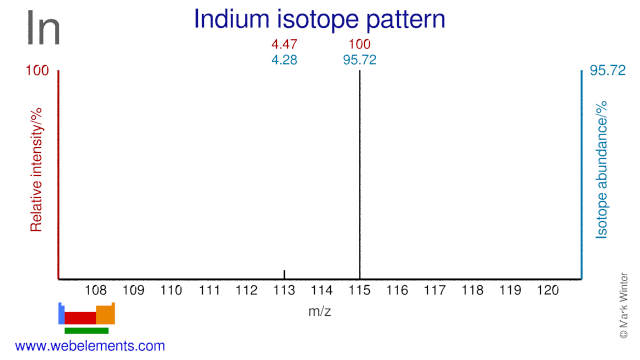
Indium has two stable isotopes and one of them, In-113, is used for the production of radioisotopes. In-113 is used for the production of Sn-113 and can also be used for the production of the medical radioisotope In-110, although the most common production route for that radioisotope is via Cd-110.
Indium: isolation
Isolation: indium would not normally be made in the laboratory as it is commercially available. Indium is a byproduct of the formation of lead and zinc. Indium metal is isolated by the electrolysis of indium salts in water. Further processes are required to make very pure indium for electronics purposes.