Platinum - 78Pt: properties of free atoms
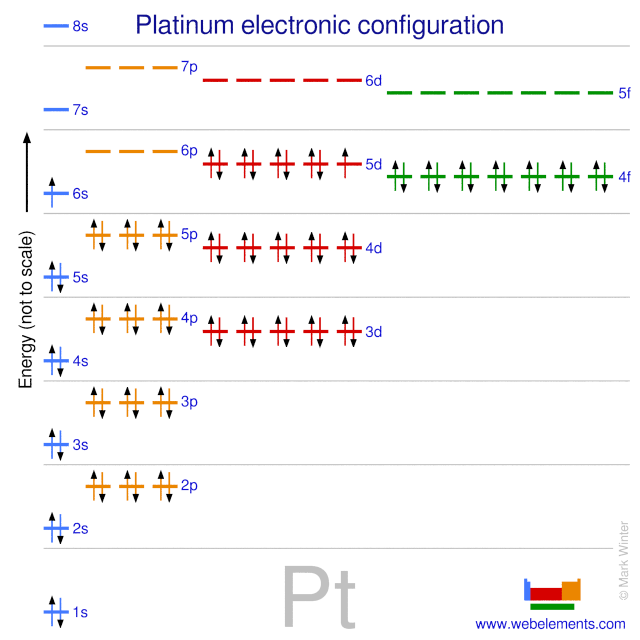
Platinum atoms have 78 electrons and the shell structure is 2.8.18.32.17.1.
The ground state electron configuration of ground state gaseous neutral platinum is [Xe].4f14.5d9.6s1 and the term symbol is 3D3.

Atomic spectrum
A representation of the atomic spectrum of platinum.
Ionisation Energies and electron affinity
The electron affinity of platinum is 205.3 2.12510(5) eV kJ mol‑1. The ionisation energies of platinum are given below.

Effective Nuclear Charges
The following are "Clementi-Raimondi" effective nuclear charges, Zeff. Follow the hyperlinks for more details and for graphs in various formats.
| 1s | 76.49 | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2s | 57.63 | 2p | 73.53 | ||||
| 3s | 54.98 | 3p | 55.89 | 3d | 64.50 | ||
| 4s | 43.64 | 4p | 42.73 | 4d | 40.63 | 4f | 39.51 |
| 5s | 26.59 | 5p | 24.42 | 5d | 19.41 | ||
| 6s | 10.75 | 6p | (no data) | ||||
| 7s | |||||||
References
These effective nuclear charges, Zeff, are adapted from the following references:
- E. Clementi and D.L.Raimondi, J. Chem. Phys. 1963, 38, 2686.
- E. Clementi, D.L.Raimondi, and W.P. Reinhardt, J. Chem. Phys. 1967, 47, 1300.
Electron binding energies
| Label | Orbital | eV [literature reference] |
|---|---|---|
| K | 1s | 78395 [1] |
| L I | 2s | 13880 [1] |
| L II | 2p1/2 | 13273 [1] |
| L III | 2p3/2 | 11564 [1] |
| M I | 3s | 3296 [1] |
| M II | 3p1/2 | 3027 [1] |
| M III | 3p3/2 | 2645 [1] |
| M IV | 3d3/2 | 2202 [1] |
| M V | 3d5/2 | 2122 [1] |
| N I | 4s | 725.4 [3] |
| N II | 4p1/2 | 609.1 [3] |
| N III | 4p3/2 | 519.4 [3] |
| N IV | 4d3/2 | 331.6 [3] |
| N V | 4d5/2 | 314.6 [3] |
| N VI | 4f5/2 | 74.5 [3] |
| N VII | 4f7/2 | 71.2 [3] |
| O I | 5s | 101.7 [2, values derived from reference 1] |
| O II | 5p1/2 | 65.3 [2, values derived from reference 1] |
| O III | 5p3/2 | 51.7 [3] |
Notes
I am grateful to Gwyn Williams (Jefferson Laboratory, Virginia, USA) who provided the electron binding energy data. The data are adapted from references 1-3. They are tabulated elsewhere on the WWW (reference 4) and in paper form (reference 5).
References
- J. A. Bearden and A. F. Burr, "Reevaluation of X-Ray Atomic Energy Levels," Rev. Mod. Phys., 1967, 39, 125.
- M. Cardona and L. Ley, Eds., Photoemission in Solids I: General Principles (Springer-Verlag, Berlin) with additional corrections, 1978.
- Gwyn Williams WWW table of values
- D.R. Lide, (Ed.) in Chemical Rubber Company handbook of chemistry and physics, CRC Press, Boca Raton, Florida, USA, 81st edition, 2000.
- J. C. Fuggle and N. Mårtensson, "Core-Level Binding Energies in Metals," J. Electron Spectrosc. Relat. Phenom., 1980, 21, 275.