Molybdenum - 42Mo: properties of compounds
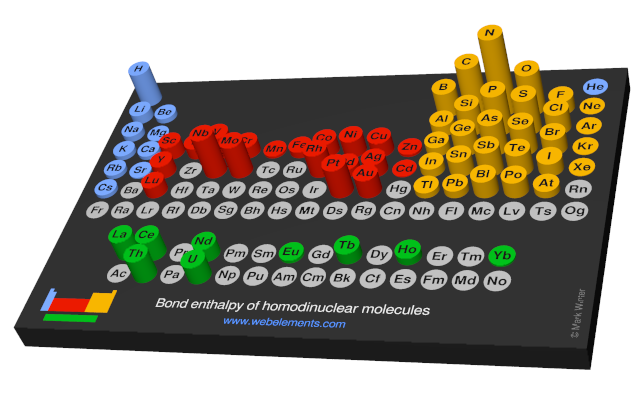
The bond energy in the gaseous diatomic species MoMo is 406 ±21 kJ mol-1.
Molybdenum: bond enthalpies in gaseous diatomic species
The following values refer to neutral heterodiatomic molecules in the gas phase. These numbers may well differ considerably from, say, single bond energies in a solid. All values are given in kJ mol-1.
| MoH | MoHe | ||||||
| MoLi | MoBe | MoB | MoC | MoN | MoO | MoF | MoNe |
| 481 ±15.9 | 560.2 ±20.9 | 464.8 | |||||
| MoNa | MoMg | MoAl | MoSi | MoP | MoS | MoCl | MoAr |
| MoK | MoCa | MoGa | MoGe | MoAs | MoSe | MoBr | MoKr |
| MoRb | MoSr | MoIn | MoSn | MoSb | MoTe | MoI | MoXe |
| MoCs | MoBa | MoTl | MoPb | MoBi | MoPo | MoAt | MoRn |
| MoFr | MoRa | ||||||
Notes
I am grateful to Professor J.A. Kerr (University of Birmingham, UK) for the provision of the bond strengths of diatomic molecules data.
The values given here are at 298 K. All values are quoted in kJ mol-1. Generally, these data were obtained by spectroscopic or mass spectrometric means. You should consult reference 1 for further details. A note of caution: the strength of, say, the C-H bond in the gaseous diatomic species CH (not an isolable species) is not necessarily, the same as the strength of a C-H bond in, say, methane.
The strongest bond for a diatomic species is that of carbon monoxide, CO (1076.5 ± 0.4 kJ mol-1). The strongest bond for a homonuclear diatomic species is that of dinitrogen, N2 (945.33 ± 0.59 kJ mol-1).
References
- J.A. Kerr in CRC Handbook of Chemistry and Physics 1999-2000 : A Ready-Reference Book of Chemical and Physical Data (CRC Handbook of Chemistry and Physics, D.R. Lide, (ed.), CRC Press, Boca Raton, Florida, USA, 81st edition, 2000.
Molybdenum: lattice energies
All values of lattice energies are quoted in kJ mol-1.
| Compound | Thermochemical cycle / kJ mol-1 | Calculated / kJ mol-1 |
|---|---|---|
| MoF3 | 5230 | 6459 |
| MoF4 | (no value) | 8795 |
| MoCl2 | 2733 | 2485 |
| MoCl3 | 5230 | (no value) |
| MoCl4 | 9573 | 8556 |
| MoBr2 | 2742 | 2448 |
| MoBr3 | 5156 | (no value) |
| MoBr4 | 9475 | 8510 |
| MoI2 | 2630 | 2422 |
| MoI3 | 5073 | (no value) |
| MoI4 | (no value) | 8427 |
| No data for any hydrides of molybdenum. | ||
| MoO2 | (no value) | 11648 |
- H.D.B. Jenkins - personal communication. I am grateful to Prof Don Jenkins (University of Warwick, UK) who provided the lattice energy data, which are adapted from his contribution contained within reference 2.
- H.D.B. Jenkins in CRC Handbook of Chemistry and Physics 1999-2000 : A Ready-Reference Book of Chemical and Physical Data (CRC Handbook of Chemistry and Physics, D.R. Lide, (ed.), CRC Press, Boca Raton, Florida, USA, 79th edition, 1998.
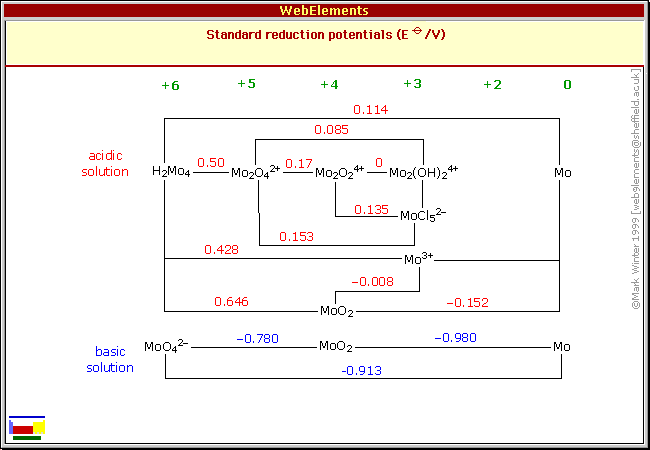
Standard Reduction Potentials
References
The standard reduction potentials given here for aqueous solutions are adapted from the IUPAC publication reference 1 with additional data and an occasional correction incorporated from many other sources, in particular, references 2-7.
- A.J. Bard, R. Parsons, and J. Jordan, Standard Potentials in Aqueous Solutions, IUPAC (Marcel Dekker), New York, USA, 1985.
- N.N. Greenwood and A. Earnshaw, Chemistry of the Elements, 2nd edition, Butterworth-Heinemann, Oxford, UK, 1997.
- F.A. Cotton and G. Wilkinson, Advanced Inorganic Chemistry, 5th edition, John Wiley & Sons, New York, USA, 1988.
- B. Douglas, D.H. McDaniel, and J.J. Alexander, Concepts and models of Inorganic Chemistry, 2nd edition, John Wiley & Sons, New York, USA, 1983.
- D.F. Shriver, P.W. Atkins, and C.H. Langford, Inorganic Chemstry, 3rd edition, Oxford University Press, Oxford, UK, 1999.
- J.E. Huheey, E.A. Keiter, and R.L. Keiter in Inorganic Chemistry : Principles of Structure and Reactivity, 4th edition, HarperCollins, New York, USA, 1993.
- G.T. Seaborg and W.D. Loveland in The elements beyond uranium, John Wiley & Sons, New York, USA, 1990.