Use the table to the right to select an adjacent element
Use the periodic table icon below for any other element
| H | ||
| Li | Be | |
|---|---|---|
| Na | Mg |
|
Use the table to the right to select an adjacent element Use the periodic table icon below for any other element |
|
|---|

|
lithium |
|---|
Here is some information about the solid state crystal structure of b-Li. Information about a second form, a-lithium is also available.
| Space group: | Im3m | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Space group number: | 229 | |||||
| Cell parameters: | a /pm | b /pm | c /pm | a° | b° | g° |
| 351.00 | 351.00 | 351.00 | 90 | 90 | 90 | |
| CrystalMaker file |
|
|---|---|
|
Mac/PCMolecule file |
|
| Chem3D file |
|
|
Chime users file |
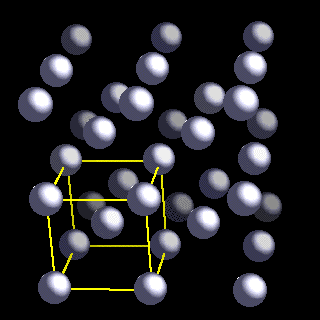
The body-centred cubic (bcc) structure is the most stable form for lithium metal at 298 K (25°C). This form is also know as b-Li. The closest Li-Li separation is 304 nm. A second form, called a-Li is most stable at low temperatures.
In the bcc lattice, every lithium atom is surrounded by eight other lithium atoms organised into a cubic array (see above Figure in which the atom coloured red is surrounded by eight lithium atoms coloured dark grey).
One way to visualize the bcc lattice is as two interlocked cubic infinite arrays of atoms. In the above Figure, the dark grey cube is part of one of these cubic arrays while the interlocked light gray cube is part of the second.
The b form is stable at room temperature and converts to the a form at low temperatures.
M.R.Nadler and C.P.Kempfer, Anal. Chem., 1959, 12, 2109.